Most web applications run thanks to MySQL databases. Aside from being free (a paid proprietary enterprise solution exists but is not required for most projects), the software is impressively reliable. It’s also easy to use and super secure.
MySQL can handle millions of queries and supports high-speed transactional processing for eCommerce websites.
The first version of MySQL appeared in 1995, and today, over ten other versions exist.
Knowing your MySQL version will help you figure out whether you need to make any configuration changes and tweak settings to keep your applications running perfectly.
This article will help you find the MySQL version via the command line.
Method 1: SSH Shell
The secured socket shell is a network protocol that allows two computers to communicate and reliably share data.
Webmasters and Database Administrators often use SSH to log into a remote computer and perform tasks on the server from anywhere. It’s basically the same as hooking up a monitor and a keyboard to the server.
SSH connections are end-to-end encrypted, so you don’t need to worry about anyone eavesdropping the communication between your computer and the remote host.
There are a couple of ways of establishing an SSH connection to your server: you can either use a client application like PuTTY, or you can do it via your operating system’s built-in command line shell. Windows users can employ PowerShell or the command prompt and Linux and MacOS have the Terminal.
To check the version your MySQL is running, type and execute mysql -V (note the uppercase V) in the command line.
MySQL will return a result that looks like this:
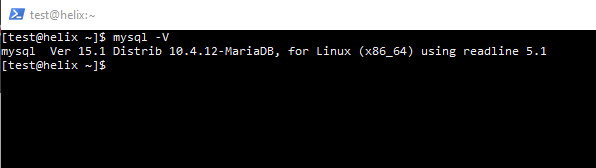
As you can see, the MySQL version for this system is 10.4.12.
Method 2: MySQL Shell
The MySQL Shell is an advanced client and code editor for MySQL. It provides scripting capabilities for JavaScript and Python and includes APIs for working with MySQL.
Webmasters use MySQL shell to perform data queries and updates, as well as various administrative operations.
To check the MySQL version from the MySQL Shell, you simply need to log into it. The command you need looks like this:
$ mysql -u [your MySQL username] -p
MySQL will ask you for the user’s password and after you enter it, it will display the version automatically.
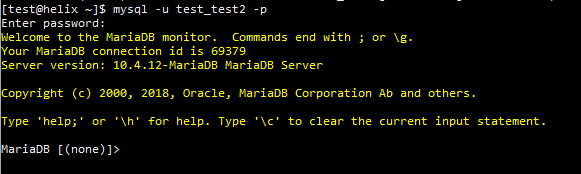
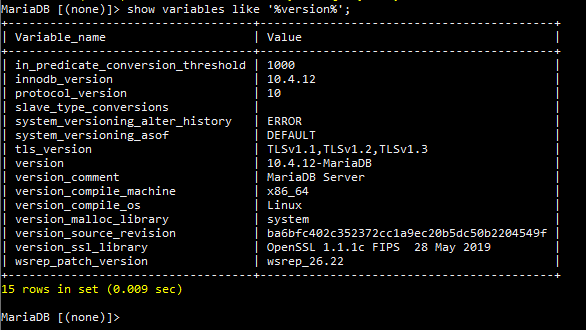
Once you’re logged in, you can also find the MySQL version using the following command:
show variables like ‘%version%’;
MySQL will return the version result after executing the command:
Understanding The MySQL Naming Scheme
Always make sure to run the latest MySQL version on your server.
Install only the latest MySQL General Availability (GA) release. The GA releases are MySQL stable versions and are safe and reliably for production uses. Although developmental releases have the newest features, they are not suitable for production uses.
MySQL 8.0.28 is the latest MySQL version.
The naming scheme uses release names that consist of three numbers and an optional suffix, for example, mysql-8.0.1-dmr.
Understanding the naming scheme will enable you to know the correct version to install. Here’s how to interpret a MySQL version number.
- The first number shows the major version number. In the above case, it’s eight.
- The second number shows the minor version number. In the example above, it’s zero. The major and minor version numbers constitute the release series number, and it describes the stable feature.
- The third number shows the number for each bug-fix release. The version with the latest bug-fix makes the best choice, of course, in most cases.
- The suffix indicates the stability level of each release. Two possible suffixes are dmr and rc. The former stands for Development Milestone Releases, while the latter stands for Release Candidate.
New features with dmr releases are not thoroughly certified for production uses.
Release Candidate is the second development stage in the series.
Although the vendors believe the RC series is relatively stable, their efforts shift to fixing bugs to stabilize the features. They might also introduce new features at this stage.
MySQL versions without any suffix are pretty stable, free of bugs and suitable for production uses. They have attained the GA status.
Wrapping It Up
Running the latest stable version of MySQL enables you to enjoy the newest features and have software free of bugs. You can always check your MySQL by following the steps we outlined above. You can always contact Support whenever you need help.
